April is Testicular Cancer Awareness Month. To highlight this occasion, we wanted to remind our readers that knowledge about this form of cancer and being aware of the common signs and symptoms can potentially save lives.
So, here is all you need to know about testicular cancer.
Testicular cancer is a disease that develops when cancerous cells grow in the tissues of the testicles. Testicles are the glands that produce sperm. They are a part of the male reproductive system. Cancer cells usually develop in one testicle, although they can also develop in both.
It is possible for testicular cancer to spread to other parts of the body through the blood or lymph vessels. Testicular cancer can form new tumors in the lungs, the liver, the stomach, the bones and even the brain. Some forms of testicular cancer can be aggressive and spread quickly if left untreated.

In some cases, testicular cancer will have no symptoms or signs at all. However, the most common symptoms include:
These symptoms may be caused by several other conditions. If you are worried about these or other symptoms you may be experiencing, consult a doctor for further testing.
Causes of testicular cancer are unknown. However, there are specific risk factors associated with testicular cancer.
You may be at greater risk of developing testicular cancer if:
When detected early, testicular cancer has a great successful treatment rate of a little over 95%. Testicular cancer also has a very high survival rate; the risk of dying is about 1 in 5,000.
For this reason, prevention is the #1 treatment of testicular cancer. Monthly self-examination is essential for all men, especially those who are at risk of developing testicular cancer. Regular self-examination will not only allow you to find potential lumps early, but it will also allow you to catch any underlying health issue as early as possible.
Here is a step by step explanation of how to perform a testicular self exam, provided by the Testicular Cancer Awareness Foundation.
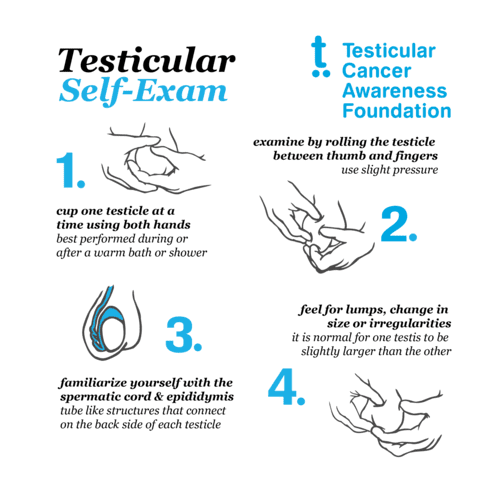
If you detect lumps during a testicular self-exam or any other kind of changes in your urological or reproductive system, make an appointment with your health care professional. Remember that early detection can save your life.
6900 Boulevard Décarie, Suite M270
Montréal, QC H3X 2T8
1100 Rue du Lux, Bureau 520
Brossard, Quebec J4Y 0E2
© 2023 Sanomed, All rights reserved. Website by Lifter
Request A Consultation Appointment
Please complete this appointment request form and we will call you back to review how to prepare, and to confirm your appointment date and time. Thanks.